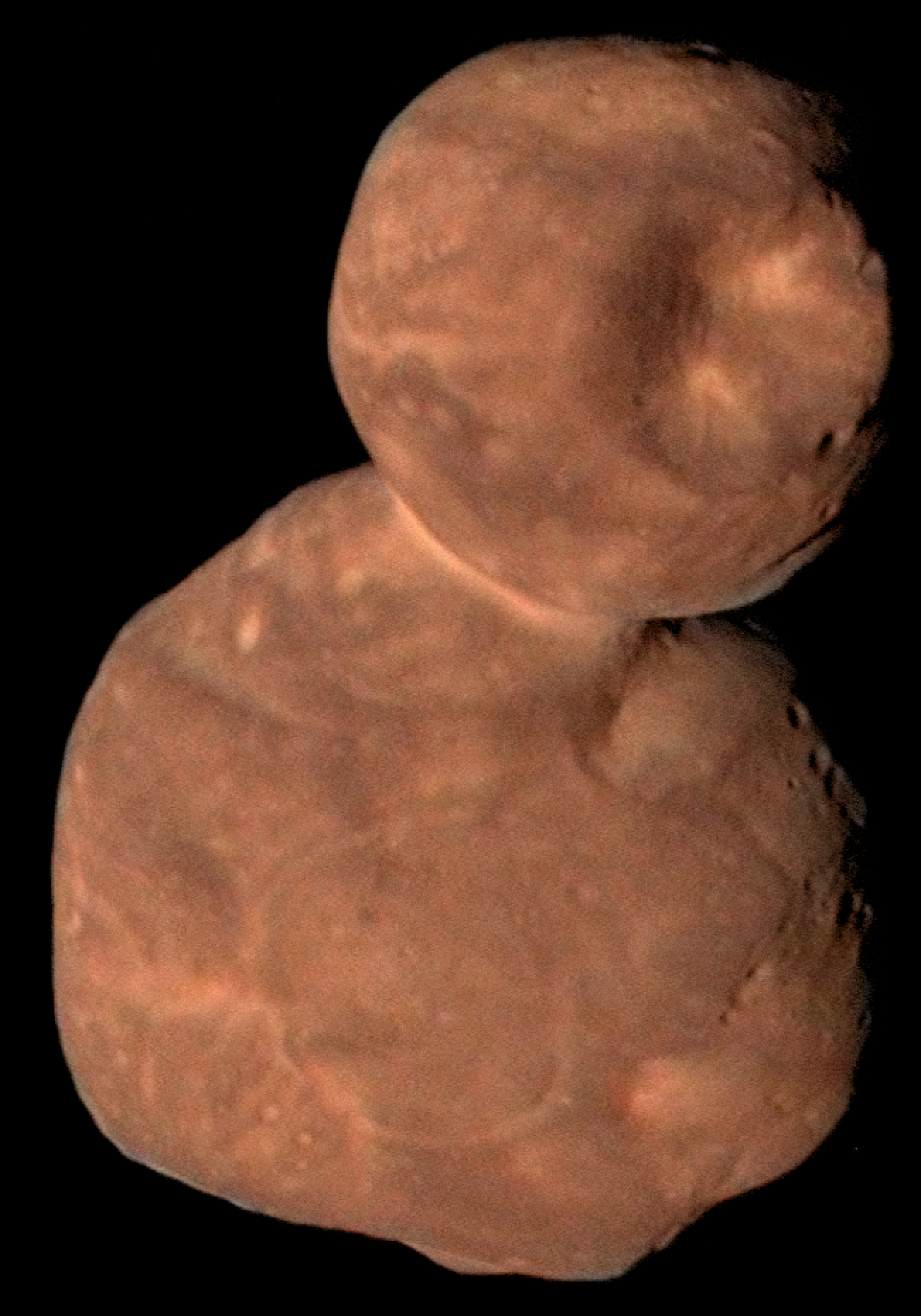
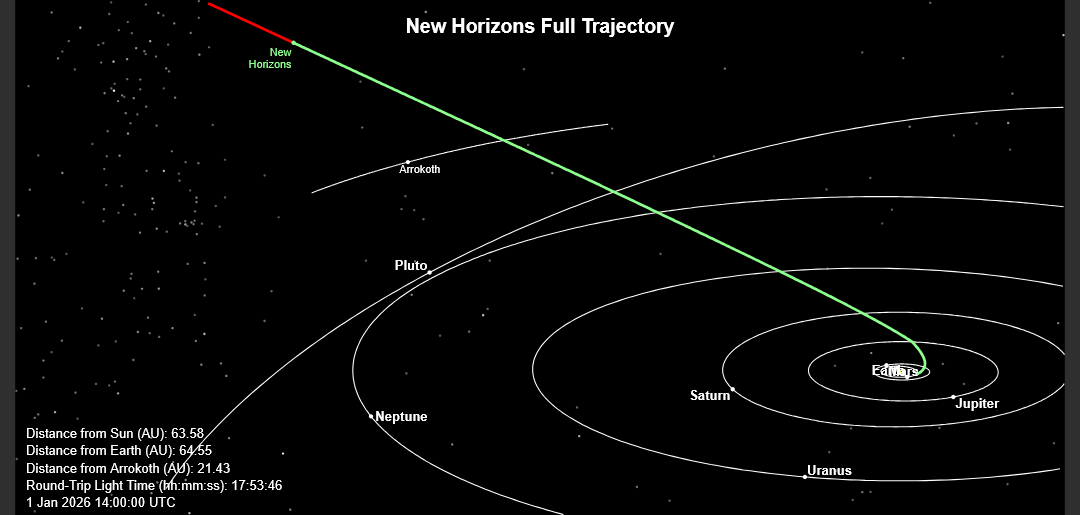
7 years ago, on New Year's Day, Jan 1, 2019, the NASA New Horizons spacecraft flew by the most distant object ever visited by a spacecraft, the contact binary trans-Neptunian object 2014 MU6, now named Arrokoth.
Arrokoth means "sky" in the Powhatan/Algonquin language.
New Horizons also saw evidence for methanol, water ice and organic molecules on the red surface of the 35 km Kuiper Belt object.
https://pluto.jhuapl.edu/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/486958_Arrokoth
Also see https://fosstodon.org/@AkaSci/111681146380738902
#NewHorizons
1/n