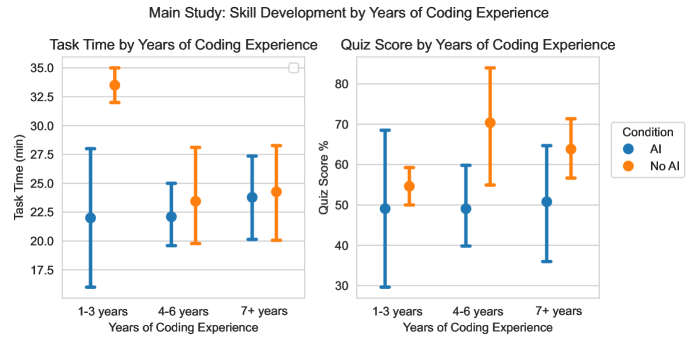
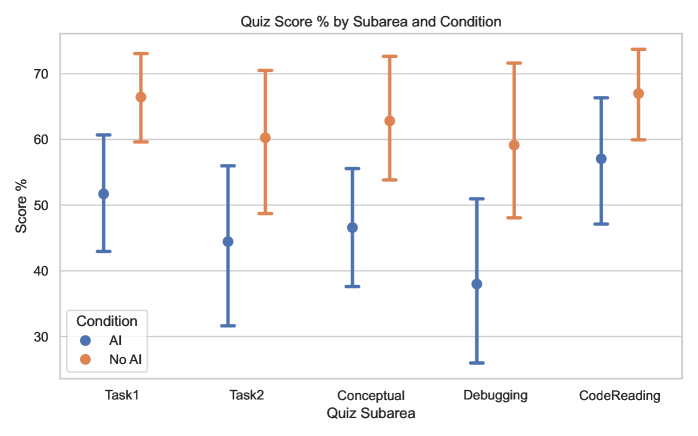
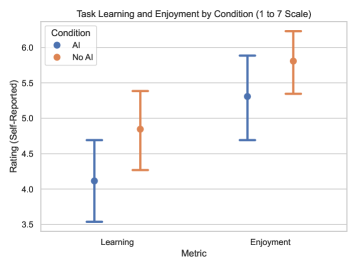
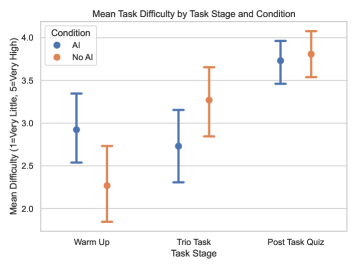
This study—from Anthropic, no less—is rather damning of the entire generative AI project. In code creation, the realm where it should shine, not only were the time gains marginal, but developers understood their code far, far less. And they didn't even have more fun doing the work!
But to me the most concerning part of this study is the fact that Anthropic could not get the control (non-AI) group to comply. Up to 35% of the "control" in the initial studies used AI tools despite instructions not to. What kind of behavior does that sound like?
UPDATE: See below for important counterpoints as to the validity of the study.